A meta-analysis suggests that tACS improves cognition in healthy, aging, and psychiatric populations
By A Mystery Man Writer
Description

A synergetic turn in cognitive neuroscience of brain diseases: Trends in Cognitive Sciences

Measured and estimated electric field magnitudes. a Field projections
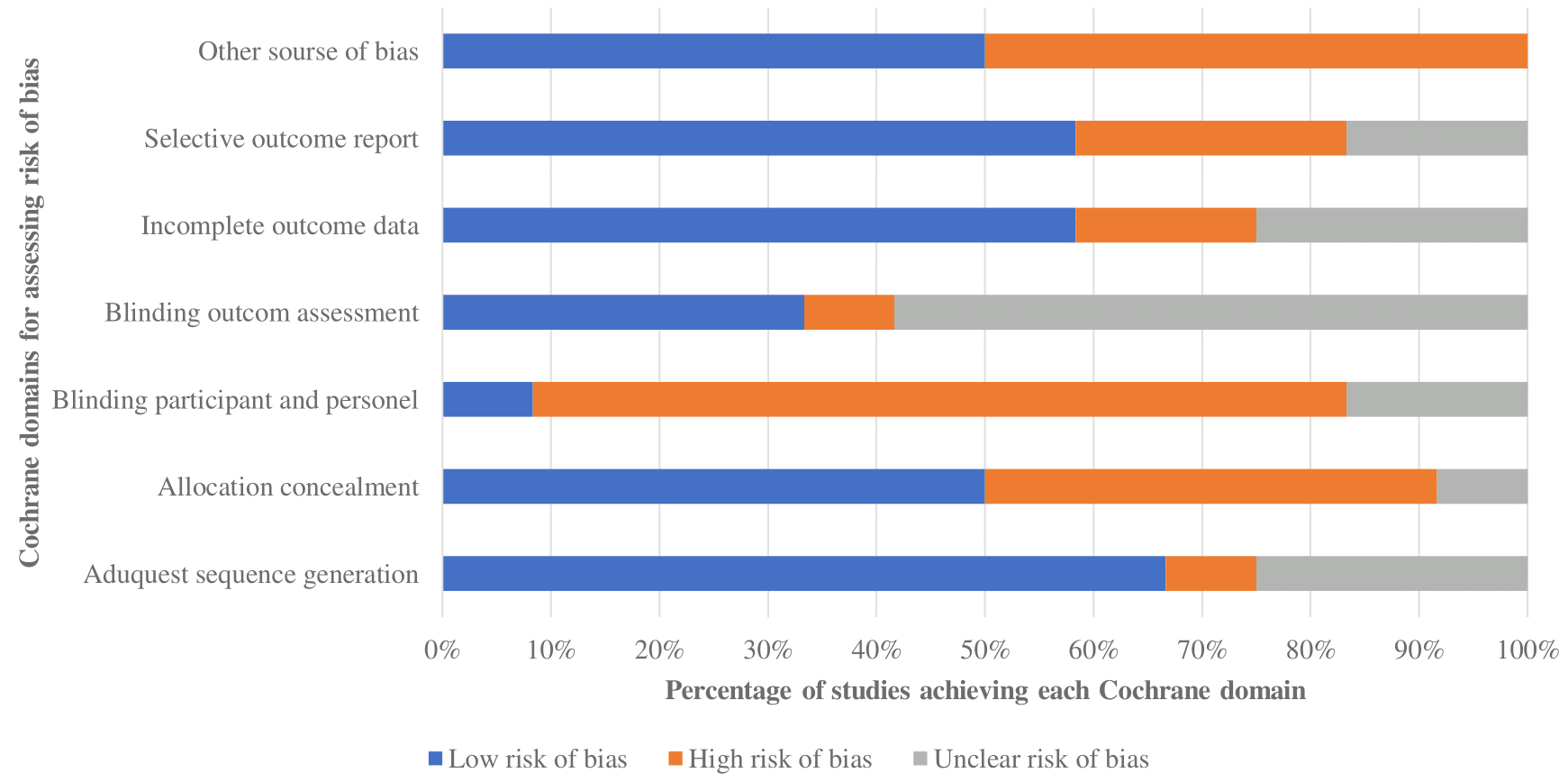
Home hazard modification programs for reducing falls in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis [PeerJ]

PDF) Neurocognitive, physiological, and biophysical effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation

In-phase tACS has no effects on behavioural performance. In this figure

Neuropsychological assessment.

Harnessing Brain Stimulation to Enhance Memory - IEEE Pulse
PDF) Conducting double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trials of transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS)

Harald Hampel, MD, PhD, MSc en LinkedIn: A meta-analysis suggests that tACS improves cognition in healthy, aging…

Brain Sciences, Free Full-Text
from
per adult (price varies by group size)







